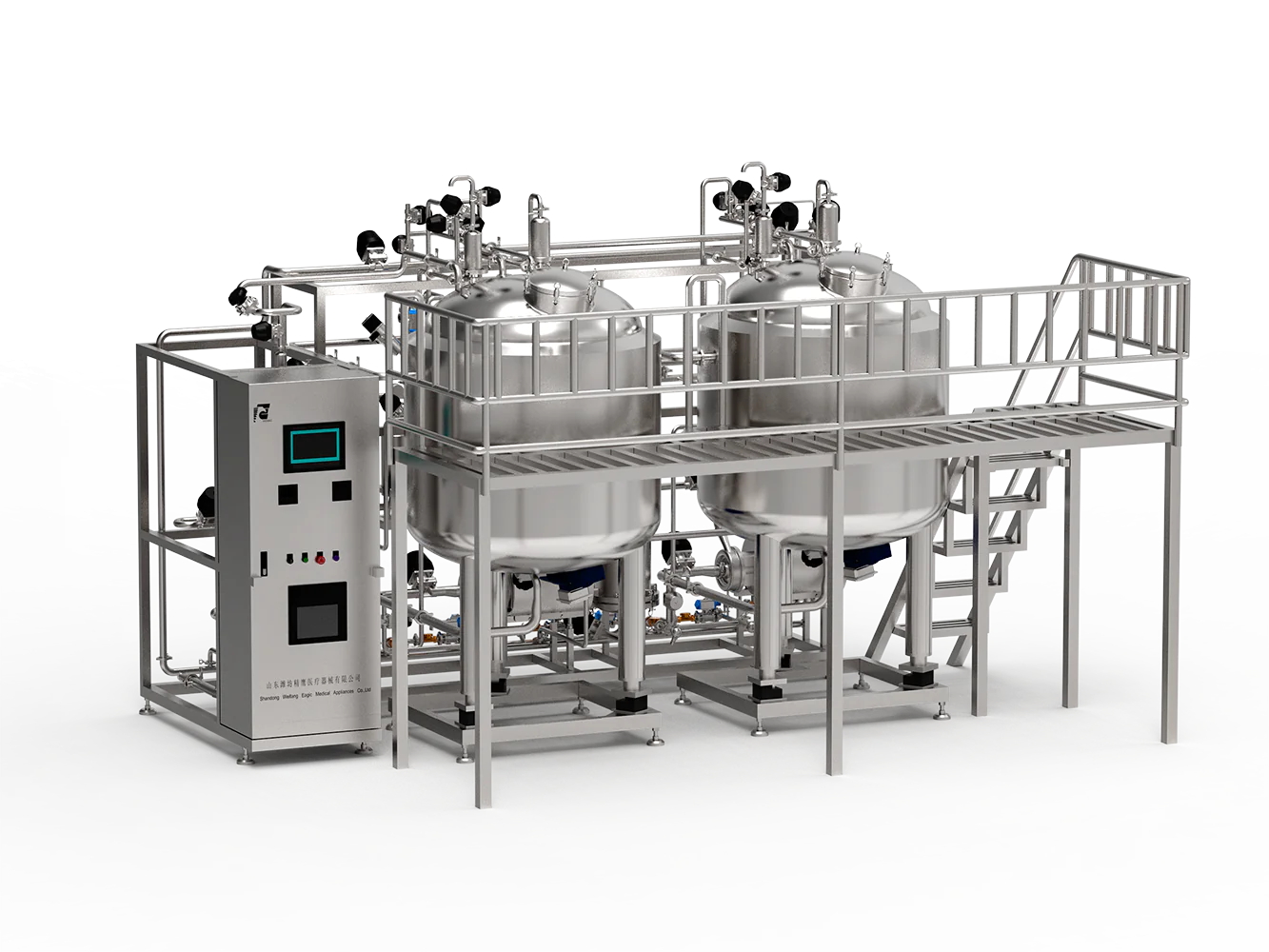
Introduction to Sterile Water Systems
A sterile water system is a critical infrastructure in healthcare, pharmaceutical processing, and water treatment facilities. It ensures the delivery of water that is free from all viable microorganisms and endotoxins, providing safe and uncontaminated water for injection, equipment sterilization, and laboratory use. Understanding the fundamentals of these systems includes appreciating their biochemical, mechanical, and hygienic principles.
The need for sterile water derives from the inherent risks associated with microbial contamination—both from pathogens and endotoxins—that can adversely affect patient safety or product quality. Thus, to meet increasingly stringent quality standards, sterile water systems combine advanced filtration, sterilization, and piping materials designed to maintain system integrity.
As part of advanced water treatment solutions, companies such as SKE & Eagle leverage decades of engineering experience to develop robust and highly reliable sterile water systems. Their manufacturing capabilities ensure compliance with industry standards, employing materials and designs that optimize system durability, ease of maintenance, and operational efficiency.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the engineering design, operation protocols, compliance regimes, and real-world applications of sterile water systems, positioning you to understand and select the optimal system tailored to your needs.
Design and Engineering Principles of Sterile Water Systems
The structural integrity and operational reliability of a sterile water system hinge on meticulous design and engineering. These systems generally consist of treatment stages, including pre-filtration, primary sterilizing filtration, ultraviolet or heat sterilization units, and carefully designed distribution piping to prevent biofilm formation and maintain sterility.
Among key design considerations:
- Material selection: Biocompatible, corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel (usually 316L) are industry standards to prevent contamination and facilitate effective cleaning.
- Filtration: Utilization of sterilizing-grade filters with nominal pore sizes of 0.2 or 0.22 microns to physically remove microorganisms without relying solely on sterilization methods.
- System layout: A closed-loop, recirculating design minimizes stagnation and maintains constant flow velocity, inhibiting microbial colonization.
- Validation points: Sensor placements and sampling ports are strategically located to monitor parameters such as temperature, pressure, and microbial load.
Diagram description: Imagine a schematic depicting a multi-stage sterile water system starting from raw water pretreatment units (carbon filters, deionizers), passing through ultra-filtration or reverse osmosis modules, followed by heat or UV sterilization chambers, then leading into a closed-loop stainless steel piping network equipped with sampling points and online microbial monitors.
Modern engineering approaches integrate automation and control systems to ensure continuous validation of sterility status, employing SCADA systems and IoT-enabled sensors. The design philosophy embodies SKE & Eagle’s commitment to system reliability and quality excellence, reflecting their core manufacturing capabilities documented in their Sterile Filter Systems portfolio.
Selection criteria when configuring a sterile water system must consider capacity, flow rate consistency, water quality input, and regulatory compliance. Additionally, engineers factor in maintainability aspects, emphasizing easy access to key components and compatibility with CIP (clean-in-place) systems.
Operation and Maintenance Best Practices
Optimal operation of a sterile water system requires adherence to rigorous maintenance protocols and continuous monitoring to sustain sterility and system performance. SKE & Eagle engineering standards specify comprehensive preventive maintenance regimens focusing on system flushing, validation, and component replacement schedules.
Key operational practices include:
- Regular sanitation: Routine cleaning cycles using validated CIP procedures maintain sterility without system disassembly.
- Monitoring parameters: Continuous measurement of flow rates, pressures, temperature, and microbial counts ensures prompt detection of deviations.
- Filter integrity tests: Employing bubble point and diffusion tests on sterilizing-grade filters verifies filter effectiveness and detects breaches.
- Documentation and traceability: Meticulous record-keeping for all maintenance activities and sensor data supports compliance and troubleshooting.
Frequent environmental monitoring at points of use and penalty points along the distribution loop gauges the presence of endotoxins and viable organisms. The role of intelligent control systems cannot be overstated; integration of automated alerts and enablement of remote parameter adjustments enhance responsive maintenance.
In practice, operators must understand the water chemistry dynamics to adjust disinfection cycles accordingly, particularly recognizing the impact of water hardness, pH, and organic load. SKE & Eagle’s technical support emphasizes training and providing detailed operational manuals aligning maintenance procedures with regulatory expectations such as USP Sterile Water for Injection Standards.
Compliance Standards and Regulatory Requirements
Sterile water systems operate at the intersection of stringent health and safety standards imposed by global regulatory authorities. Understanding and complying with these frameworks is paramount for system design, validation, and operation.
The following are core regulatory references that dictate quality benchmarks:
- United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Sterile Water for Injection standards: Establish requirements for microbial content, endotoxin limits, and testing protocols.
- European Pharmacopeia (Ph. Eur.): Regulations on sterility testing and water quality for pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- FDA CGMP Guidelines: Enforce the good manufacturing practice including design control and preventive maintenance of sterile water systems.
- ISO 9001 and ISO 13485: Quality management certifications relevant to medical device water systems.
Companies like SKE & Eagle integrate these stringent regulations into their engineering and manufacturing practices, ensuring each sterile water system not only meets but often exceeds baseline compliance. Their alignment with validation standards—including Design Qualification (DQ), Installation Qualification (IQ), Operational Qualification (OQ), and Performance Qualification (PQ)—strengthens system reliability and traceability.
The documentation supporting compliance covers water source validation, sterilization validation, microbial monitoring protocols, and risk assessment analysis. Furthermore, pharmaceutical customers benefit from SKE & Eagle’s adherence to validation lifecycle processes documented in their validation support offerings.
Applications and Use Cases of Sterile Water Systems
The versatility of sterile water systems extends across multiple domains where absolute water purity and sterility are imperatives:
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing: Sterile water is essential for parenteral drug preparation, equipment sterilization, and formulation processes.
- Healthcare facilities: Critical for patient dialysis, surgical instruments rinsing, and intravenous infusions.
- Biotechnology production: Ensures contamination-free environments in cell culture and fermentation processes.
- Laboratories and research centers: Provides high purity water for biochemical reactions, analytical instruments, and microbiology incubators.
- Medical device sterilization: Used in rinsing and sterilizing devices to maintain compliance with hygiene standards.
Engineers designing systems for each application tailor parameters such as flow rate, loop size, sterilization methods, and monitoring permutations to meet specific process requirements. For example, sterile water for injection (WFI) production demands rigorous heat or membrane sterilization steps, often integrated with high-purity water systems such as those provided by SKE & Eagle’s comprehensive range.
The adaptability of SKE & Eagle’s sterile water filtration units facilitates integration into existing infrastructure as well as new builds, minimizing downtime and ensuring quality assurance. Their engineering teams collaborate closely with facility designers to optimize layout for both performance and regulatory compliance.
Incorporating real-time microbial sensors and online endotoxin monitoring in distributed systems marks the cutting edge of use cases, enhancing safety and reducing manual sampling frequency.
Common Myths and Misconceptions About Sterile Water Systems
Despite extensive use and formalized standards, several misconceptions about sterile water systems persist in engineering and operational circles. Addressing these myths is essential to avoid costly errors and optimize system performance.
Myth 1: Sterile water systems require no maintenance once installed.
Reality: Like all critical infrastructure, sterile water systems demand scheduled maintenance, validation, and monitoring to sustain sterility and functionality. Ignoring maintenance can lead to microbial breakthrough and system failure.
Myth 2: A single sterilization method suffices for complete sterility assurance.
Reality: Modern systems employ multiple barriers including filtration, heat or UV sterilization, and hygienic piping designs to ensure comprehensive microbial control, as recommended by standards and demonstrated in SKE & Eagle’s multi-modal solutions.
Myth 3: Sterile water is synonymous with purified water.
Reality: While purified water is treated to remove most impurities, sterile water undergoes additional sterilization to eliminate all living microorganisms and endotoxins, making it suitable for injection or sensitive medical uses.
Myth 4: Sterile water systems are only needed in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Reality: Sterile water plays a vital role across healthcare, biotechnology, and research laboratories; any environment requiring aseptic conditions benefits from these systems.
Awareness of such misconceptions enhances system design integrity and operational protocols.
Innovations in Sterile Water Systems by SKE & Eagle
SKE & Eagle continuously advances sterile water system technology by integrating digitalization, smart materials, and modular design philosophies into their products. Their systems exemplify a balance between engineering rigor and practical usability.
Among the company’s technology highlights:
- Advanced Filtration:** Utilization of high-efficiency sterilizing-grade membrane filters which provide reliable microbiological barriers while reducing flow resistance.
- Modular System Architecture:** Facilitates scalable installation and minimizes downtime during maintenance or expansion.
- Smart Monitoring Solutions:** Integration of IoT-enabled sensors directly linked to centralized control units allowing proactive management of water quality parameters in real time.
- Industry 4.0 Enabled Services: Remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance services help clients optimize system uptime and reduce lifecycle costs.
The engineering and manufacturing excellence embedded in these sterile water systems benefit from SKE & Eagle’s ISO-certified production workflows and their dedication to sustainability and energy efficiency.
To explore more about SKE & Eagle’s filtration and water treatment technologies in the context of sterile water applications, visit their Filtration Solutions page.
Frequently Asked Questions
What defines a sterile water system?
A sterile water system is engineered infrastructure that delivers water completely free from viable microorganisms and endotoxins, typically utilizing sterilizing-grade filtration, sterilization methods like heat or UV, and sanitized piping to maintain continuous sterility for medical or pharmaceutical use.
How does SKE & Eagle ensure the quality of sterile water systems?
SKE & Eagle ensures quality by adhering to strict engineering standards, employing premium materials such as 316L stainless steel, validating system performance through IQ/OQ/PQ processes, and incorporating advanced filtration and sterilization technologies tailored to comply with global regulatory norms.
What are common applications for sterile water systems?
Sterile water systems are widely used in pharmaceutical manufacturing, healthcare for dialysis and infusion, biotechnology production lines, research laboratories, and medical device sterilization, ensuring aseptic conditions and patient safety.
What maintenance is required to keep a sterile water system operational?
Regular maintenance includes scheduled sanitation cycles via CIP, filter integrity testing, continuous monitoring of temperature and microbial counts, pressure validation, timely component replacements, and documentation to validate system performance and compliance.
How do regulatory standards affect sterile water system design?
Regulatory standards such as USP, FDA CGMP, and ISO certifications mandate specific water quality parameters, validation protocols, materials, and monitoring requirements, directly influencing system design to ensure sterility is reliably maintained and documented.
Contact and Further Inquiries
For expert advice on sterile water systems, or to explore how SKE & Eagle’s advanced water treatment technologies can support your facility’s needs, please reach out via the following channels:
- Facebook: Connect with SKE & Eagle on Facebook
- Email: info@ske-eagle.com
You are also encouraged to fill out the contact form at the bottom of the official website for personalized consultation and more detailed technical information regarding sterile water systems and related solutions.